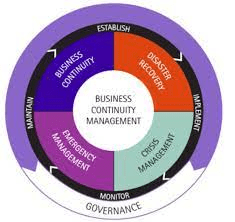
Certainly! ISO 22301:2019 is the international standard for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS). It provides a framework for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve a business continuity management system. The primary goal is to enhance an organization’s resilience and ability to respond effectively to disruptions.
Here are key aspects of ISO 22301:2019:
Overview:
- Title: ISO 22301:2019 – Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Requirements
- Published: October 2019
Key Principles and Requirements:
- Context of the Organization:
- Understanding the organization’s external and internal context.
- Identifying interested parties and their requirements.
- Leadership:
- Demonstrating leadership and commitment to the BCMS.
- Appointing a Business Continuity Manager with appropriate authority.
- Planning:
- Identifying business continuity objectives and determining the risks and opportunities.
- Establishing a business continuity policy and developing a framework to achieve objectives.
- Support:
- Providing the necessary resources and support for the BCMS.
- Competence, awareness, and communication regarding business continuity.
- Operation:
- Implementing and operating the BCMS processes.
- Establishing a business impact analysis (BIA) and risk assessment.
- Performance Evaluation:
- Monitoring, measuring, analyzing, and evaluating the BCMS performance.
- Conducting internal audits and management reviews.
- Improvement:
- Taking actions to continually improve the effectiveness of the BCMS.
- Addressing non-conformities and conducting corrective actions.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Resilience:
- Organizations can better identify and understand potential threats and disruptions.
- Improved Response and Recovery:
- Defined processes and procedures ensure a more organized and efficient response during disruptions.
- Stakeholder Confidence:
- Demonstrating commitment to business continuity can enhance trust among customers, partners, and other stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Adherence to ISO 22301 may assist organizations in meeting legal and regulatory requirements related to business continuity.
- Cost Savings:
- Proactive business continuity management can minimize the financial impact of disruptions.
Certification Process:
- Gap Analysis:
- Evaluate existing practices against ISO 22301 requirements.
- Implementation:
- Establish and implement processes and procedures according to the standard.
- Internal Audit:
- Conduct internal audits to ensure compliance with the standard.
- Certification Audit:
- An accredited certification body performs an external audit to assess compliance.
- Certification:
- If the organization meets the requirements, ISO 22301 certification is granted.
Continuous Improvement:
- Monitoring and Review:
- Regularly review the BCMS to ensure its ongoing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
- Updating the BCMS:
- Adjust processes based on changes in the organization, its context, and lessons learned from disruptions.
Remember, for the most accurate and up-to-date information, always refer to the latest version of the ISO 22301 standard and consult with accredited certification bodies or experts in business continuity management.
What is required ISO 22301 :2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
ISO 22301:2019 specifies requirements for a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) to help organizations establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their business continuity capabilities. Here is a summary of the key requirements outlined in ISO 22301:2019:
1. Context of the Organization (Clause 4):
- 4.1 Understanding the Organization and its Context:
- Identify external and internal issues relevant to the BCMS.
- 4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties:
- Identify interested parties and their requirements related to business continuity.
2. Leadership (Clause 5):
- 5.1 Leadership and Commitment:
- Demonstrate leadership and commitment to the BCMS.
- Appoint a Business Continuity Manager.
3. Planning (Clause 6):
- 6.1 Actions to Address Risks and Opportunities:
- Establish a risk management process for addressing risks and opportunities.
- 6.2 Business Continuity Objectives and Planning to Achieve Them:
- Set business continuity objectives.
- Develop plans to achieve these objectives.
4. Support (Clause 7):
- 7.1 Resources:
- Provide necessary resources for the BCMS.
- 7.2 Competence:
- Ensure that personnel have the necessary competence.
- 7.3 Awareness:
- Promote awareness of the importance of business continuity.
- 7.4 Communication:
- Establish and maintain internal and external communication related to business continuity.
5. Operation (Clause 8):
- 8.1 Operational Planning and Control:
- Establish, implement, and maintain processes for business continuity.
- 8.2 Business Impact Analysis and Risk Assessment:
- Conduct a business impact analysis (BIA) and risk assessment.
6. Performance Evaluation (Clause 9):
- 9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, and Evaluation:
- Monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate the performance of the BCMS.
- 9.2 Internal Audit:
- Conduct internal audits of the BCMS.
- 9.3 Management Review:
- Review the BCMS by top management.
7. Improvement (Clause 10):
- 10.1 General:
- Continually improve the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the BCMS.
- 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action:
- Address nonconformities and take corrective actions.
Certification Process:
- Gap Analysis:
- Assess the current state against ISO 22301 requirements.
- Implementation:
- Establish and implement processes and procedures aligned with the standard.
- Internal Audit:
- Conduct internal audits to ensure compliance.
- Certification Audit:
- An accredited certification body performs an external audit to assess compliance.
- Certification:
- If the organization meets the requirements, ISO 22301 certification is granted.
Organizations are encouraged to refer to the complete ISO 22301:2019 standard for detailed information and specific requirements. Additionally, seeking guidance from experts and accredited certification bodies can help ensure a smooth and effective implementation of the Business Continuity Management System.
Who is required ISO 22301 :2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
ISO 22301:2019 is a voluntary international standard for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS), and its adoption is not mandatory. Organizations often choose to implement ISO 22301 for various reasons, including:
- Customer and Stakeholder Expectations:
- Some organizations, especially those in industries where business continuity is critical (e.g., finance, healthcare, information technology), may choose to adopt ISO 22301 to meet customer expectations or comply with industry best practices.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- In certain industries or regions, there might be regulatory requirements related to business continuity. Implementing ISO 22301 can help organizations align with these regulatory expectations.
- Risk Management:
- Organizations concerned about potential disruptions, whether from natural disasters, cybersecurity threats, or other risks, may adopt ISO 22301 to enhance their resilience and ability to respond effectively.
- Competitive Advantage:
- Having an ISO 22301 certification can be a differentiator in the marketplace, signaling to customers and partners that the organization is committed to maintaining continuity in the face of disruptions.
- Supply Chain Requirements:
- Larger organizations may require their suppliers and partners to have a certified BCMS as part of their risk management and supply chain continuity strategies.
- Organizational Requirements:
- Some organizations may recognize the importance of having a systematic approach to business continuity and decide to implement ISO 22301 as part of their overall management system.
Steps for Adoption:
- Commitment from Leadership:
- Leadership commitment is crucial for the successful implementation of ISO 22301. Top management should endorse and support the initiative.
- Gap Analysis:
- Assess the current state of business continuity within the organization against the requirements of ISO 22301.
- Implementation:
- Develop and implement the necessary processes, procedures, and documentation to meet the standard’s requirements.
- Training and Awareness:
- Ensure that employees are trained and aware of their roles in supporting the BCMS.
- Internal Audits:
- Conduct internal audits to assess the effectiveness of the BCMS and identify areas for improvement.
- Certification Audit:
- Engage with an accredited certification body to undergo a certification audit.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Regularly review and improve the BCMS based on lessons learned, changes in the organization, and evolving risks.
While ISO 22301 is not a legal requirement in most cases, organizations may choose to adopt it based on their specific needs, industry context, and risk management priorities. If an organization decides to pursue ISO 22301 certification, it is important to work with accredited certification bodies to ensure a credible and recognized certification process.
When is required ISO 22301 :2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
ISO 22301:2019, which outlines the requirements for a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS), is a voluntary standard. It is not mandatory for organizations to adopt ISO 22301. However, there are various situations and considerations that may prompt or benefit organizations in adopting this standard:
- Customer or Stakeholder Requirements:
- Some customers or stakeholders may require their suppliers or partners to have a certified BCMS in place. This is common in industries where business continuity is critical, such as finance, healthcare, or technology.
- Industry Best Practices:
- Organizations operating in industries where disruptions could have significant consequences often choose to adopt ISO 22301 as a best practice for managing business continuity.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- In certain sectors or regions, regulatory authorities may require organizations to have a structured approach to business continuity. ISO 22301 can help demonstrate compliance with such regulations.
- Risk Management:
- Organizations that want to enhance their resilience to potential disruptions, including natural disasters, cyber threats, or other risks, may adopt ISO 22301 as part of their risk management strategy.
- Competitive Advantage:
- Having ISO 22301 certification can be a competitive advantage, signaling to customers, partners, and stakeholders that the organization is committed to maintaining continuity in the face of disruptions.
- Supply Chain Requirements:
- Larger organizations may require their suppliers and partners to have a certified BCMS to ensure the resilience of the entire supply chain.
- Organizational Requirements:
- Some organizations recognize the importance of having a systematic and structured approach to business continuity and choose to implement ISO 22301 as part of their overall management system.
- Public or Stakeholder Perception:
- Certification to ISO 22301 can enhance an organization’s reputation by demonstrating a proactive approach to managing disruptions and ensuring the continuity of critical operations.
- Insurance or Risk Mitigation:
- Some insurance companies may offer favorable terms to organizations with certified BCMS, recognizing the reduced risk associated with a structured approach to business continuity.
While ISO 22301 is not a legal requirement in most cases, organizations may find value in adopting it based on their specific needs, industry context, and risk management priorities. If an organization decides to pursue ISO 22301 certification, it’s important to work with accredited certification bodies to ensure a credible and recognized certification process.
Where is required ISO 22301 :2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
The requirement for ISO 22301:2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) can arise from various factors and is not universally mandated by law. Instead, the need for ISO 22301 certification is often driven by specific circumstances, industry expectations, customer demands, or regulatory requirements. Here are some scenarios where ISO 22301 certification might be required or strongly recommended:
- Industry-Specific Regulations:
- In certain industries or sectors, regulatory authorities may require organizations to have a robust business continuity management system. ISO 22301 can be used to demonstrate compliance with such regulatory requirements.
- Customer or Contractual Requirements:
- Some customers, especially in critical sectors like finance, healthcare, and technology, may include ISO 22301 certification as a prerequisite for business contracts or partnerships. It serves as a way for organizations to assure their clients that they have effective business continuity measures in place.
- Supply Chain Expectations:
- Larger organizations may require their suppliers and business partners to obtain ISO 22301 certification to ensure the resilience of the entire supply chain. This is particularly common in industries where disruptions can have cascading effects.
- Risk Management Practices:
- Organizations that prioritize robust risk management and resilience strategies may adopt ISO 22301 as a recognized standard to structure and formalize their business continuity efforts.
- Insurance Considerations:
- Some insurance companies may consider ISO 22301 certification favorably when determining premiums or offering coverage. Certification can demonstrate an organization’s commitment to minimizing business interruption risks.
- Competitive Advantage:
- Certification to ISO 22301 can provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace, especially when customers are looking for suppliers or partners with strong business continuity practices.
- Global or Multinational Operations:
- Organizations with operations in multiple countries may find ISO 22301 certification beneficial for demonstrating a standardized and internationally recognized approach to business continuity.
- Public and Stakeholder Expectations:
- In certain cases, organizations may choose to obtain ISO 22301 certification to meet the expectations of the public, stakeholders, or shareholders who value a commitment to business continuity.
It’s important for organizations to assess their specific context, industry requirements, and stakeholder expectations to determine whether ISO 22301 certification is necessary or beneficial. Certification is generally voluntary, but the decision to pursue it is influenced by a combination of regulatory, contractual, and strategic considerations. If an organization decides to pursue certification, they should work with accredited certification bodies to ensure a credible and recognized certification process.
How is required ISO 22301 :2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
Implementing and obtaining certification for ISO 22301:2019, the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS), involves several steps. Below is a general guide on how an organization can achieve compliance with ISO 22301:
1. Understanding ISO 22301:2019:
- Familiarize yourself with the requirements of ISO 22301:2019. Obtain a copy of the standard and ensure that key personnel understand its principles.
2. Leadership and Commitment:
- Demonstrate leadership commitment to business continuity.
- Appoint a Business Continuity Manager or designate responsibilities to ensure accountability.
3. Establishing the Context:
- Identify the external and internal context of the organization.
- Determine the interested parties and their relevant requirements.
4. Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and Risk Assessment:
- Conduct a Business Impact Analysis to identify critical processes and their dependencies.
- Perform a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities.
5. Business Continuity Objectives and Plan:
- Set business continuity objectives based on the BIA and risk assessment.
- Develop a business continuity plan outlining how to respond to disruptions.
6. Resources and Competence:
- Allocate necessary resources to support the BCMS.
- Ensure that personnel have the necessary competence for their roles.
7. Communication and Awareness:
- Establish communication processes for internal and external stakeholders.
- Create awareness programs to educate employees about business continuity.
8. Documentation and Record Keeping:
- Develop and maintain documented information as required by ISO 22301.
- Keep records of activities related to the BCMS.
9. Testing and Exercising:
- Conduct regular testing and exercising of the business continuity plan to ensure its effectiveness.
10. Monitoring and Measurement:
- Establish processes for monitoring and measuring the performance of the BCMS.
- Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the effectiveness of business continuity measures.
11. Internal Audits:
- Conduct internal audits to evaluate compliance with ISO 22301 requirements.
- Identify areas for improvement through the audit process.
12. Management Review:
- Hold regular management reviews to assess the performance of the BCMS.
- Make decisions regarding potential improvements.
13. Continuous Improvement:
- Use the outputs of internal audits, management reviews, and testing to continually improve the effectiveness of the BCMS.
14. Certification Process:
- Engage with an accredited certification body.
- Undergo a certification audit to assess compliance with ISO 22301 requirements.
15. Certification Decision:
- Based on the certification audit, the certification body will make a decision regarding certification.
16. Maintaining Certification:
- Continuously maintain and improve the BCMS to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 22301.
It’s essential to tailor the implementation process to the organization’s specific context, risks, and objectives. Organizations may seek the guidance of business continuity experts or consultants and work with accredited certification bodies throughout the process. Certification is typically valid for a specific period, and organizations must undergo regular surveillance audits to maintain certification.
Case Study on ISO 22301 :2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
Certainly! Let’s consider a fictional case study of a company, ABC Corporation, implementing and obtaining certification for ISO 22301:2019 Business Continuity Management System (BCMS).
Case Study: ABC Corporation – ISO 22301 Certification
Background:
ABC Corporation is a multinational technology company with operations in multiple countries. Recognizing the critical importance of business continuity, ABC decided to implement ISO 22301 to enhance its resilience and ensure the uninterrupted delivery of products and services.
Implementation Process:
- Leadership Commitment (Clauses 5 and 6):
- Top management at ABC Corporation demonstrated commitment to business continuity by appointing a dedicated Business Continuity Manager and establishing a cross-functional BCMS team.
- Understanding the Organization and Context (Clause 4):
- ABC identified key external and internal factors affecting its business continuity, including supply chain dependencies, regulatory requirements, and potential risks.
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and Risk Assessment (Clause 8):
- A comprehensive BIA was conducted to identify critical processes and dependencies.
- A risk assessment was performed to evaluate potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Business Continuity Planning (Clause 8):
- ABC developed a business continuity plan outlining response and recovery procedures for various scenarios identified in the risk assessment.
- Training and Awareness (Clause 7):
- Employees received training on their roles and responsibilities in the event of a disruption.
- An awareness campaign was conducted to educate employees about the importance of business continuity.
- Documentation and Record Keeping (Clause 7):
- Documented information, including policies, procedures, and records, was created and maintained as required by ISO 22301.
- Testing and Exercising (Clause 8):
- Regular testing and exercising of the business continuity plan were conducted to ensure its effectiveness.
- Lessons learned from tests were used to refine and improve the plan.
- Internal Audits (Clause 9):
- Internal audits were conducted to assess compliance with ISO 22301 requirements.
- Non-conformities were identified and addressed through corrective actions.
- Management Review (Clause 9):
- Regular management reviews were held to evaluate the performance of the BCMS.
- Decisions were made to allocate resources and drive continual improvement.
Certification Process:
- Certification Decision (Clause 10):
- ABC engaged with an accredited certification body for an external audit.
- The certification body assessed ABC’s compliance with ISO 22301 requirements.
- Certification Outcome:
- ABC Corporation successfully achieved ISO 22301 certification.
- The certification body issued a certificate recognizing ABC’s commitment to business continuity.
Post-Certification:
- Continuous Improvement (Clause 10):
- ABC continued to monitor and improve its BCMS based on ongoing risk assessments, internal audits, and management reviews.
- Feedback from incidents and exercises was used to refine and enhance business continuity processes.
Results and Benefits:
- Enhanced Resilience:
- ABC Corporation significantly improved its ability to respond effectively to disruptions, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuity of critical operations.
- Stakeholder Confidence:
- ISO 22301 certification instilled confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders, showcasing ABC’s commitment to business continuity.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- ABC remained in compliance with relevant industry regulations related to business continuity.
- Competitive Advantage:
- ISO 22301 certification provided ABC with a competitive advantage in the marketplace, differentiating it as a reliable and resilient business partner.
This case study illustrates how ABC Corporation successfully implemented ISO 22301, obtained certification, and continually improved its business continuity practices to navigate disruptions effectively. The process involved strong leadership commitment, risk assessments, planning, testing, and ongoing monitoring for continuous improvement.
White Paper on ISO 22301 :2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS)
Creating a comprehensive white paper on ISO 22301:2019 Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) involves detailing the standard’s requirements, benefits, implementation guidelines, and best practices. Below is an outline for a white paper on ISO 22301:
Title: “Navigating Business Disruptions: A Guide to ISO 22301 – Business Continuity Management Systems”
Executive Summary:
Introduce the importance of business continuity in today’s dynamic business environment and how ISO 22301 serves as a valuable framework for organizations seeking to enhance resilience.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Brief overview of the ISO 22301 standard.
- The importance of business continuity in modern enterprises.
- Understanding ISO 22301:2019
- Overview of the ISO 22301 standard.
- Key principles and requirements.
- Benefits of ISO 22301 Certification
- Enhanced resilience and risk management.
- Improved stakeholder confidence.
- Regulatory compliance.
- Competitive advantage.
- ISO 22301 Implementation Process
- Leadership commitment and establishing a BCMS team.
- Context analysis and risk assessment.
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and risk management.
- Business continuity planning and development.
- Resources, training, and awareness.
- Testing, Monitoring, and Continuous Improvement
- Regular testing and exercising of business continuity plans.
- Monitoring and measurement of BCMS performance.
- Internal audits and management reviews.
- Incorporating lessons learned for continual improvement.
- Certification Process
- Engaging with certification bodies.
- External audit process.
- Certification decision and issuance.
- Case Studies
- Real-world examples of organizations benefiting from ISO 22301 certification.
- Challenges and Best Practices
- Common challenges in implementing ISO 22301.
- Best practices for overcoming challenges.
- Conclusion
- Summary of key points.
- Encouragement for organizations to adopt ISO 22301.
- Resources and Further Reading
- Links to relevant ISO documents.
- Recommended reading and resources for implementing ISO 22301.
Conclusion:
Summarize the critical points discussed in the white paper, emphasizing the benefits of ISO 22301 certification and encouraging organizations to prioritize business continuity.
Additional Materials:
Include any relevant charts, diagrams, or infographics that illustrate key concepts, statistics on business continuity, or the certification process.
This white paper aims to provide organizations with a comprehensive understanding of ISO 22301:2019, guiding them through the implementation process and highlighting the benefits of achieving certification. Organizations can use this resource to enhance their business continuity efforts and navigate disruptions effectively.